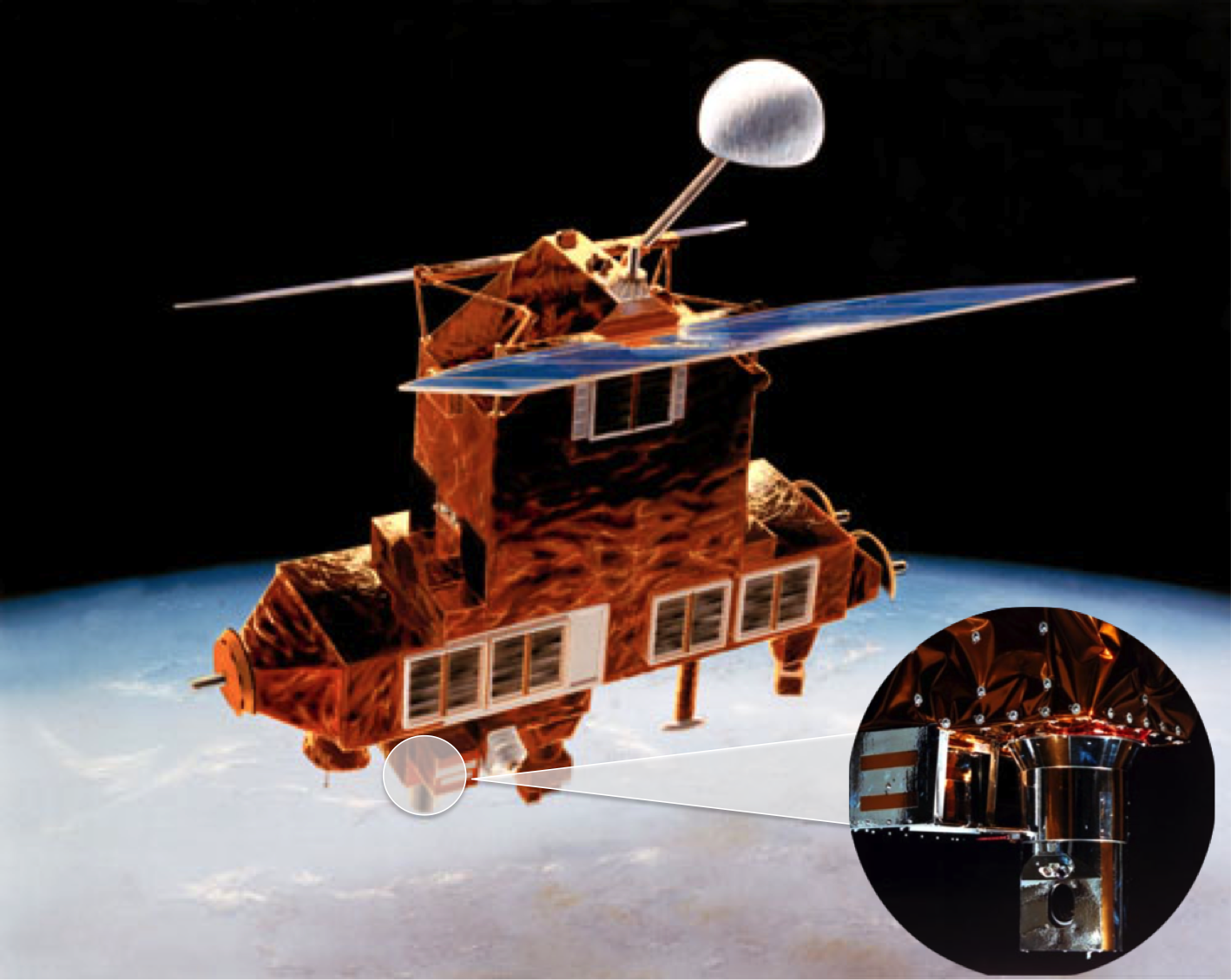
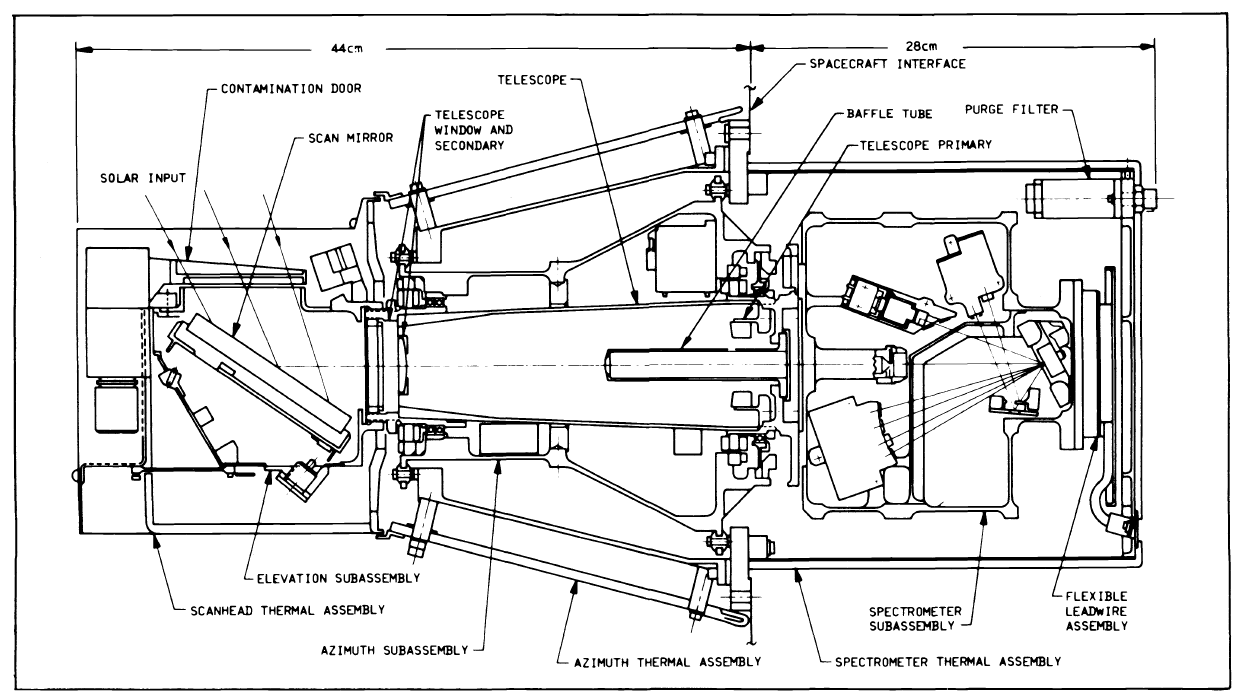
SAGE II (Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment II) was launched aboard the Earth Radiation Budget Satellite (ERBS) in October 1984. During each sunrise and sunset encountered by the orbiting spacecraft, the instrument used the solar occultation technique to measure stratospheric aerosols, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and water vapor.
SAGE II continued the SAGE measurements of stratospheric ozone from 1984-2005. This long-term, stable data set has proven invaluable in determining trends in ozone.
Data from SAGE II, in conjunction with data from sister instruments SAM II and SAGE I, can be used to estimate long-term constituent trends and identify responses to episodic events such as volcanic eruptions.
The data SAGE II collected was integral to confirming human-driven changes to ozone, and thus contributed to the 1987 Montreal Protocol that banned certain harmful chemicals. SAGE II also saw that ozone stopped decreasing in response to this action.
Major results from SAGE II include illustrations of the stratospheric impact of the 1991 Mount Pinatubo eruption, identification of a negative global trend in lower stratospheric ozone during the 1980s, and quantitative verification of the positive water vapor feedback in current climate models.